NIAMEY - After bust-ups with Mali and Burkina Faso, France is now watching its relationship with Niger spiral downwards following the Sahel's third military takeover in as many years.
The same scenes that have played out in Niger since the July 26 coup have been eerily witnessed in its two neighbours, where elected leaders were tossed aside in 2020 and 2022.
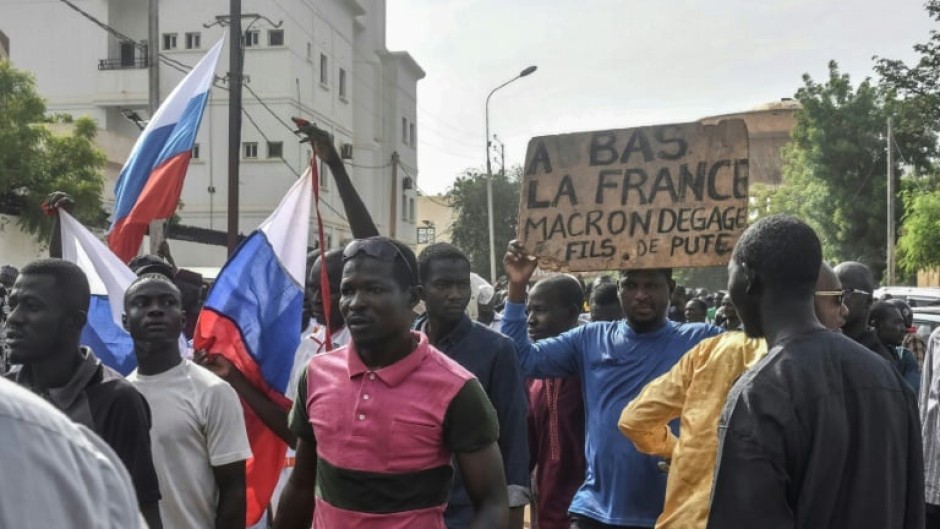
In each event, France -- the former colonial power and ally in the fight against jihadism -- becomes the target of crowds chanting anti-French and pro-Russian slogans, followed by verbal broadsides from the new junta.
President Mohamed Bazoum, a linchpin in France's strategy in the Sahel, was overthrown last Wednesday by members of his guard.
A day after hostile demonstrations outside the French embassy triggered a warning from Paris, the putschists on Monday accused France of seeking to "intervene militarily" by plotting with the head of Niger's National Guard.
Coups in the Sahel "are supported by a fringe of the population which have already shown a hostile attitude to French or Western presence," said Ibrahim Yahaya Ibrahim, a researcher with the International Crisis Group (ICG) think tank.
"Anti-French talk, or anti-French politics, have been around for a long time," a study published last month by the French Institute of International Relations (IFRI) said last month.
"However, they are no longer limited as they were in the past to the intellectual elite but have also spread extensively among the working classes, particularly in urban areas."
In the capital Niamey, a stronghold of Bazoum opponents, there seemed scant support for France's policies in Niger even before the coup.
France was accused of failing to eliminate jihadists who had been rampaging across the country since 2015, and attacked for a diplomatic style deemed opaque or arrogant.
- Disinformation campaign -
Against this background -- and in a country where some two-thirds of the population are illiterate -- conspiracy theories have flourished.

"Opinion is widespread in the public that French troops are only going to conflict zones to provide arms for the jihadists," Rahmane Idrissa, a researcher at the African Studies Centre at the Netherlands' University of Leyden, said on his personal blog.
This idea "is not based on facts but on feelings, and sadly you don't counter feelings by offering factual proof."
Countries in the Sahel have become an information battleground, with Russia accused by France of leading a campaign of denigration.
Bazoum took a risk by agreeing to host France's reconfigured anti-jihadist force in the Sahel, which quit Mali last year after the Bamako regime brought in Russian paramilitaries.
"Bazoum teamed up with France over the head of public opinion," said Nigerien analyst Amadou Bounty Diallo.
In November 2021, a French military convoy that was pulling out of Mali was blocked by demonstrators at Tera, in western Niger.
Three of them were killed, by shots that the Nigerien government attributed to French troops.
- Election hopes -
"Mr. Bazoum was unable to clearly show the Nigerien public that he had an independent relationship with western partners -- in public opinion, he looked like someone who was very close to France," said Ibrahim.
Bazoum was feted internationally after winning elections in 2021, opening the way to Niger's first-ever peaceful transition of power.
He won in a second-round runoff with 55 percent of the vote, defeating an opposition that had criticised ties with France deemed too cosy and complicit.
France is a major provider of financial aid to Niger, which has since been suspended, but trade ties these days are "extremely thin", said Alain Antil, head of the Sub-Saharan African Centre at the IFRI think tank.
"Niger is no longer a strategic partner for uranium, as it was able to be in the 1970s and 80s," he said.

